
In this document, terms such as hard and soft bounce are defined. Below are details regarding how Aimbase processes and handles these delivery results and what they mean for long-term email delivery.
Definitions
Hard Bounce: A hard bounce in the context of email communication refers to a situation where an email cannot be delivered to the intended recipient and is returned to the sender due to a permanent or persistent issue. This typically occurs when the recipient's email address is invalid, nonexistent, or blocked. Hard bounces indicate a permanent problem with the email address and are unlikely to be resolved by simply re-sending the email.
Soft Bounce: A soft bounce in the context of email communication refers to a situation where an email is temporarily unable to be delivered to the recipient's inbox but might still have a chance of being successfully delivered at a later time. Unlike a hard bounce, which indicates a permanent issue, a soft bounce is typically caused by temporary problems that prevent the email from reaching its destination. Soft bounces are often related to issues on the recipient's side or with their email server.
Example Bounce Reasons
Reasons why a hard bounce might occur:
Invalid Email Address: The email address is incorrectly formatted, contains typos, or doesn't follow the standard email address structure (e.g., missing "@" symbol).
Nonexistent Domain: The domain part of the email address (the part after "@" symbol) doesn't exist or is no longer active.
Blocked Address: The email server has blacklisted the sender's domain or IP address, preventing the email from being delivered.
Inactive Account: The recipient's email account has been closed, deactivated, or marked as inactive.
Mail Server Configuration Issues: The recipient's mail server might have misconfigured settings or technical issues that prevent email delivery.
Reasons why a soft bounce might occur:
Recipient's Mailbox Full: The recipient's mailbox is temporarily full and cannot accept new messages until space is cleared.
Temporary Server Issues: The recipient's mail server might be experiencing high traffic, technical problems, or maintenance, causing the email delivery to be delayed.
Message Size Exceeded: The email's size might exceed the recipient's server limits, causing the email to bounce back.
Recipient's Email Server Offline: The recipient's email server might be temporarily offline or unreachable.
Content Filtering: The recipient's email server might have strict content filtering rules that prevent certain types of emails from being delivered.
DNS Resolution Issues: Temporary issues with DNS (Domain Name System) resolution can lead to email delivery failures.
It's important to note that while soft bounces are temporary in nature, repeated occurrences to the same email address might eventually lead to a classification as a hard bounce if the issues are not resolved over time.
Email service providers and email marketing platforms usually track soft bounces and provide information about the reasons for the bounce. Monitoring and addressing soft bounces is important to maintain good email deliverability and sender reputation. If a soft bounce persists over multiple delivery attempts, it might be worth investigating the issue further or reaching out to the recipient to ensure the email address is still valid and operational.
How Aimbase Handles Bounces
When it comes to temporary or soft bounces, Aimbase retries delivery for up to 8 hours in the following intervals: 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours. A soft bounce is not final and Aimbase retries until the email is either delivered or failed, which is the final status.
To clarify further, if the message fails to be delivered on each subsequent retry attempt, the message will then fail permanently and the "Too Old" error message will be displayed, this will be on the 8th attempt. If that occurs, it will be logged as an event like the one below on the details page of a Subscriber record. This data can be accessed from the Subscribers Grid.
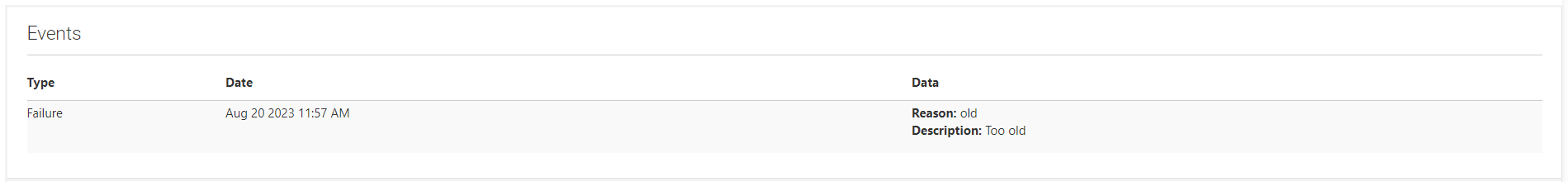
Once an email address is deemed a hard bounce from an email send, the email address will be updated to have a Bounce status of Hard Bounce within any list in Aimbase on which it appears. Any subsequent email sending attempts to that email address willl be reflected as Skipped - Bounced for that email address in the Subscribers Grid.
Summary
Hard Bounce:
- Permanent Issue: A hard bounce occurs when an email cannot be delivered to the recipient due to a permanent issue. This means the email will never be successfully delivered to that recipient's inbox.
- Causes: Hard bounces are typically caused by factors like an invalid email address, nonexistent domain, blocked sender, or a closed/deactivated recipient mailbox.
- Action: It's important to remove email addresses that result in hard bounces from your email list to maintain good sender reputation and deliverability. This action should take place within Aimbase automatically as the system processes the results of previous sends to each email address.
Soft Bounce:
- Temporary Issue: A soft bounce occurs when an email cannot be delivered to the recipient temporarily due to issues that might be resolved over time.
- Causes: Soft bounces can result from reasons like a full recipient mailbox, temporary server problems, message size issues, or content filtering.
- Action: Soft bounces don't necessarily require immediate action, but monitoring and addressing repeated soft bounces to the same address are important to ensure successful email delivery.